Hello. And welcome to this ApexSQL Unit Test general overview video.
ApexSQL Unit Test is a SQL Server Management Studio add-in used to manage SQL database unit tests. Besides the set of predefined tests and a demo kit that includes a sample database and a set of sample unit tests, ApexSQL Unit Test can be used to create, maintain, and run unit tests against any database and even run tests on multiple databases on the same SQL Server as well as on multiple SQL Server instances at the same time.
Once the ApexSQL unit test is installed and integrated into SQL Server Management Studio, let's initiate the Unit Test Explorer tab, which is the main communication channel between the add-in and databases that contain unit tests. We'll do that either by clicking on the Unit Test Explorer command from the add-in toolbar or by using a keyboard shortcut.
By default, the Demo Kit dialog appears, offering the user to install sample database and demo kit. Let's check both options and click the Create button. This will create two databases, tsqlt_Example and PUBS_QA. Both databases will have a tSQLt framework already installed and a set of predefined unit tests.
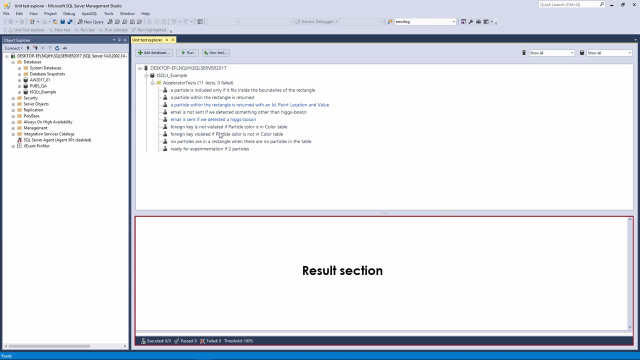
Before moving forward with the demo kit, let's explain the structure in the Unit Test Explorer tab. It is organized in such a way that each SQL Server instance is a top node. When expanding a SQL Server node, all databases that contain the tSQLt framework will be shown. Expanding any database shows test classes in which SQL unit tests are grouped. And finally, expanding each test class shows all underlying unit tests.
Now we can easily determine what is what in the Unit Test Explorer tab. We can confirm that for the tsqlt_Example database, there are 11 unit tests all within a single test class called AcceleratorTests. To run any unit test, we can simply right-click on it and select the Run option from the context menu. Note that the unit test name will invert its color on a right-click. This indicates that it is selected for execution.
In order to run multiple tests from the same class, left-click the ones that will be executed and use the right-click to initiate the execution process. The same can be achieved using the Run button above.
Running tests from different classes is not allowed no matter if it is within the same database or SQL Server instance or not. In the case where at least one test from another class is selected, the add-in displays a message that multiple tests can be executed only if they belong to the same class.
Similar to running one or more tests within a single class, each node in the Unit Test Explorer tab has its own Run command. Initiating the Run command on the particular node will execute all underlying tests.
Once a unit test or a group of unit tests are executed, the Results section at the bottom of the Unit Test Explorer tab shows the test summary and messages related to the unit tests that did not pass. For instance, if we execute all unit tests for the PUBS_QA database, the Results section shows 87% of tests passed while 13% failed. Since the PUBS_QA database has 15 unit tests specified, that would be 13 passed tests and two failed. This information will be displayed in the Results section.
Execution results can be exported to an XML document, SQL script, or even in a database. Above the summary, the appropriate messages will be shown for unit tests that failed. These are the messages that a developer will specify in the unit test itself to be shown in case the test fails. As soon as unit tests are executed at least once, each test will have the appropriate icon so the user can easily verify if it failed or passed.
Similar to the Run command on each node, the Refresh command will reset the status to the initial state for the selected node by right-clicking it and choosing the Refresh command from the context menu.
Besides the set of predefined tests, new test classes and tests can be added for any database. In order to create a new test class, we'll need to right-click a database in the Unit Test Explorer tab and choose the New Class option from the context menu. After specifying a name for a new class, it appears in the Unit Test Explorer tab for the selected database.
Now that we have a new class, we can add new unit tests. In order to do so, we'll right-click a newly created class and choose the New Test command from the context menu. This initiates the new test dialog, where the test class will be set to already point to the newly created class. We'll specify a name for the new test. Note that the "test" prefix is mandatory for all the tests.
Once we click the OK button, a new query opens with a unit test template script. Since each unit test is a SQL-stored procedure, it is important to mention that a unit test must be created using ApexSQL Unit Test and the described workflow. SQL-stored procedures created outside ApexSQL Unit Test will not be recognized as unit tests.
Let's see how to add an existing database in the Unit Test Explorer tab. In order for a database to be added in the Unit Test Explorer tab, it must have the tSQLt framework installed. We'll use AdventureWorks database for the purpose of this video. If a database does not have the tSQLt framework installed, the context menu in the object explorer pane will have only one option. And that is to install the tSQLt framework.
When installing the tSQLt framework, the user can choose to install the integrated version, to browse the file system to determine if the specific version was previously downloaded, or to pick a specific version directly from the web. Since, in our case, the integrated version is
 07:41
07:41
