Hello and welcome to this ApexSQL Script general overview video. ApexSQL Script is a SQL server development tool which can script databases into scripts, scripts folders, deployment packages, and commit directly to source control projects. ApexSQL Script also supports scripting from SQL Azure databases and Amazon RDS for SQL server.
ApexSQL script can also automate and schedule database scripting using the command line interface or CLI, script both SQL database objects and data, consolidate multiple SQL scripts into one script, script an entire SQL server database down to individual columns, easily decrypt encrypted SQL database objects, and much more.
ApexSQL Script also supports picking specific SQL database objects and data for scripting, along with automatically including dependent objects and creating executable installation packages that end users can run without installing any other software. ApexSQL Script consists of two main components-- a Windows application used for manual SQL database scripting selecting, specific SQL database objects and data, and various options for the scripting process, a console application which allows users to schedule and automate SQL database scripting and to run everything unattended.
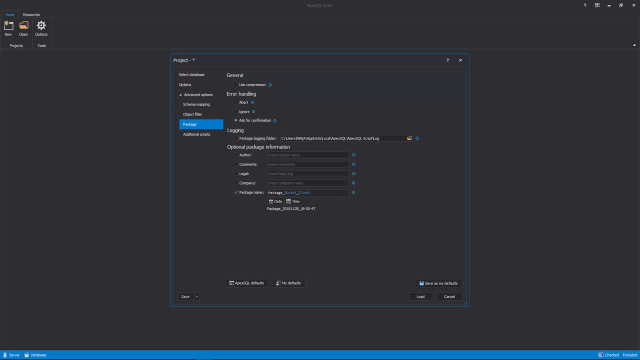
On application startup, the main application window will be shown along with the new project window. Select database is the first tab in the new project window. And here, one or multiple databases can be checked for the scripting process after connecting to a desired SQL server. The next tab in the New Project window is the Options tab, in which various options can be set for the structure, data, owners and script, optional output elements, and header and footer.
Also, additional tabs with their options can be set with a click in the Advanced Option tab. The first is the Schema Mapping tab. Here, on the left side in the Schema Mapping Pairs list, original schema names will be shown from a loaded database, while on the right side schema names are shown for the script that will be created and those that can be edited. In addition, new schema mapping pairs can be added or existing ones can be removed from the list.
The next tab is the Object Filter tab in which specific object types, or objects, can be included or excluded for the scripting process. To see all objects for a specific object type, just click on it in a left tree view panel. And all objects for that object type will be shown in the right panel list. Additionally, Object Selection can be saved in a file with the click on Export button. And later on, it can be used for the same or similar databases with the Import button.
The Package tab contains options for package installers such as use compression, error handling, logging, and optional package information. The last tab is the Additional Script tab, in which pre or post-processing scripts can be set to be executed before or after the scripting process. These scripts can be loaded with the Use this script option, or typed in with the Use embedded script option.
Now, when all options are set, click the Load button in the bottom right corner of the new project window. And the selected database with all of its objects and data will be shown in the main application window. By default, the Structure view is selected with a list of all objects, which can be further filtered using the simple check option in the list, selecting which objects will be included in the scripting process.
Additionally, the Object filter panel on the left side can filter shown object types in the list by unchecking the undesired ones. Or the filter editor can be initiated to filter out specific object types based on the filter conditions for object name or schema. If there is a need to include data in the scripting process, switch to the Data view with a click on the Data button from the Home tab.
If data needs to be included, make sure that the same tables are checked in both Structure and Data views in order to script them correctly. If there is a need to script specific data, there are three ways to achieve it. Switch to the View tab and click the Columns filter button, and the Column filter panel will be shown. For each selected table in the date of view, all its columns are shown in the Columns filter panel.
If there are some columns that don't need to be scripted, just uncheck them. For each table under the Max column, a new maximum value of scripted rows can be set by directly entering it into the Max cell or with a right-click on the cell and choosing the Edit max value command. For example, if there are 20 rows and the max value is set to 5, only the first five rows will be included in the generated script.
The last filter mechanism is the Where clause filter, which can be initiated with a click of an ellipse button in the Where cell, or by selecting the Edit SQL Where clause command from the right-click context menu. In the Where clause window for the selected table, specify a desired condition that will limit the number of rows that will be included in the scripting process. After the condition is entered, click the Apply button. And it will instantly show the new row count.
Once everything is set and selected, click the script button from the Home tab to initiate the Script wizard. In the first step of the Script wizard, the scripting mode should be chosen. And in this example, Structure and Data is selected. In the second step, the output type should be chosen. And it can be selected between five different output types. 1, SQL script. 2, Scripts folder. 3, Source control project. 4, C# solution. And 5, Executable installer.
In this case, the source control output type is chosen. The next step is the dependency step in which, by default, all dependent objects that were not checked
 09:21
09:21
